Today we’re taking another dive into OEM Mazda parts to better understand how they function. Specifically, OEM suspension springs, since there are CorkSport Lowering Springs coming soon for the 2018+ Mazda 6 2.5T. While a simple concept, springs are very important to the handling, appearance, and comfort of your vehicle.

The new Mazda 6 Turbo uses a lot of the same components as the GEN 3 Mazda 3 and Mazda 6, however, the suspension has been optimized for the new “premium” feel and to deal with the extra weight that comes when adding a turbo. The SkyActiv chassis has primarily remained the same though, with the same MacPherson strut front suspension and multi-link rear suspension shown below.
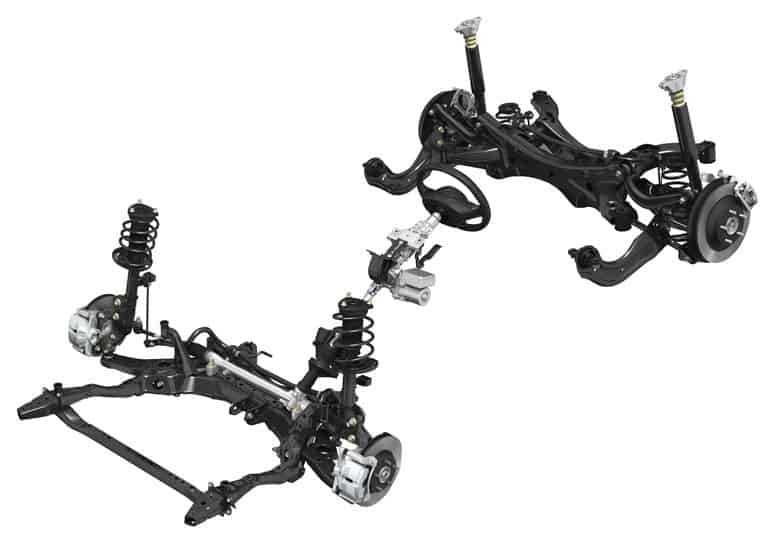

Now, onto the springs themselves; both the front and rear suspension of the Mazda 6 use standard compression springs. The spring’s job is to support the weight of the vehicle when at rest and adsorb impacts when hitting bumps or going quickly around a corner. That’s it. Seems simple enough right? Since the springs are the parts of the suspension that “suspends” the vehicle though, their characteristics and how they interact with the rest of the suspension system are critical.
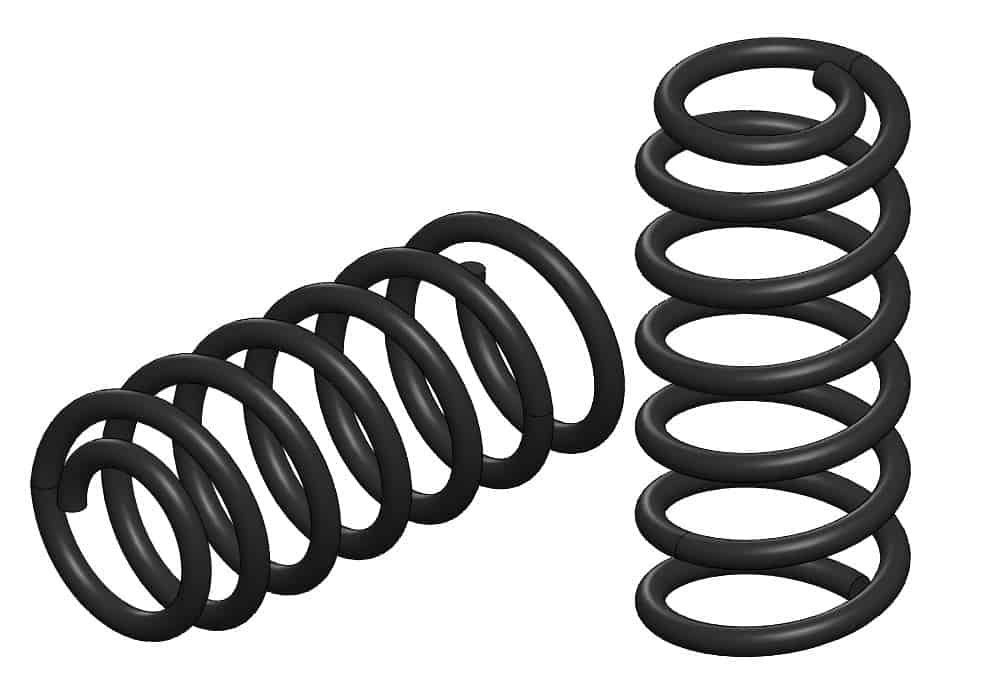

There are two main characteristics that define a spring: rate and free length. Both are pretty easy to understand. Free length is simply the length of the spring with no weight or force acting on it. So set a spring by itself on a table, measure how tall it is, and there’s your free length.
Spring rate is a little more complex, as it is the measure of how much weight it takes to compress a spring a given distance. So, if you have the same weight and put it on two different springs the one with the higher rate will compress less. The rate is usually measured in kg/mm (often shortened to K) or lbs/in.
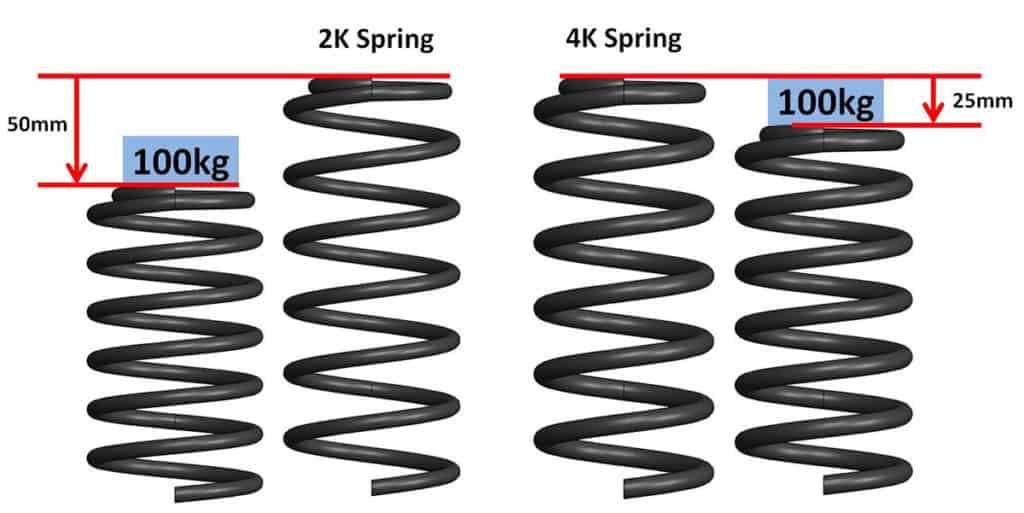
For example, if you had a 2K spring and a 4K spring and applied 100kg to each, the 2K would compress 50mm and the 4K would only compress 25mm.
What do these measures mean for your car though? If we keep the rate the same but only change the free length, the shorter the spring, the lower the car. For a given car, a spring can be too short, causing poor ride (sitting on the bump stops all the time), or the risk of a spring coming out of place, causing noises or at worst, the spring falling out of the vehicle.
If we change the spring rate and leave the free length the same, things are a little more complicated. The higher the rate, the stiffer the ride is, plus your ride height will increase. Since the weight of the car is not changing, the higher rate spring will now compress less when the car sits on it, meaning your car sits higher at rest. Too large of a rate and your OEM shocks cannot keep up causing a bouncy ride, and vice-versa if too soft you are hitting

Now that the basics are covered, let’s look specifically at the Mazda 6 2.5T. The OEM springs give a good ride as to be expected (likely very soft spring rates) as this can be a huge issue for potential customers if the car ride quality is harsh. Handling is decent overall but has a few quirks. When going around a corner quickly, the car rolls over onto the rear springs excessively before settling and getting through the corner. When at the limit of traction, the car understeers severely, like most cars sold today.
Finally, the ride height is pretty high, likely to prevent any issue with driveways saying hello to the new front fascia. Interestingly, the MZ6T sits a little higher in the rear; we think it ensures enough suspension travel in case there’s a full load of passengers and a full trunk.

For further analysis, we also had the OEM springs tested for rate and ended up with the following: 3.05K front, 5.05K rear. While these numbers are fairly arbitrary right now, they are a necessary data point to have when designing lowering springs. These rates also contradict a very common misconception. Many people think that because there is less weight in the rear of a front-wheel drive car, the spring rates must be softer in the rear for a good ride & handling. This is simply not true in most cases, after all why would Mazda do the opposite? Due to the design of the rear suspension, the spring is basically being pushed on by a lever. This means the spring needs to be stiffer in order to support the same amount of weight as if the lever wasn’t there.
So overall, the OEM springs are good, but have plenty of room for improvement. I just touched the surface of suspension design and as we go through more of this project we’ll get into dampers, natural frequency, and much more. Stay tuned for more info and if you have any questions, don’t be afraid to ask! Check out the release blog for the Mazda 6 lowering springs.
-Daniel @ CorkSport
Connect with us
You may also like
- Mazda 6 Turbo Lowering Springs Release!
- 2018-2021 Mazda 6 Turbo Lowering Springs 2.0
- Ride The Unicorn with the CorkSport 3rd Gen Mazda 3 & Mazda 6 Turbo Kit
- Mazda 6 Turbo Down Pipe


